

Forever Free, No Registration.
Free & Full Support Service.
and this is what makes traffic quality, real users!
From chrome on each active user's pc.
Visit with browser under rule control.
Chrome Core, No Virus No Trojan.
Filter Sound, Block Pop-ups.
Professional Team, Continual Upgrade.
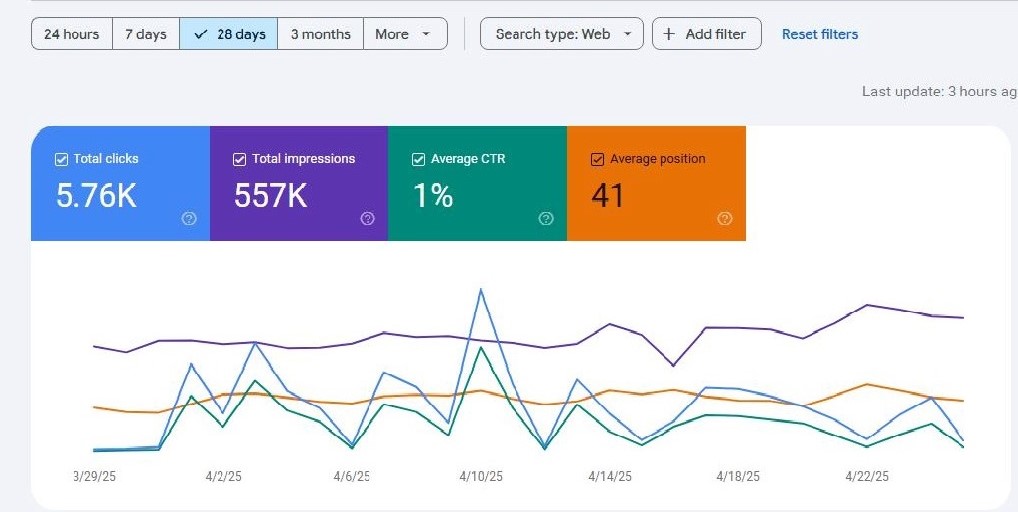
Fast Traffic is a powerful traffic exchange tool designed to boost your website visits organically and efficiently. Whether you're growing a blog, promoting an offer, or building brand awareness, Fast Traffic helps you reach real users in a real environment.
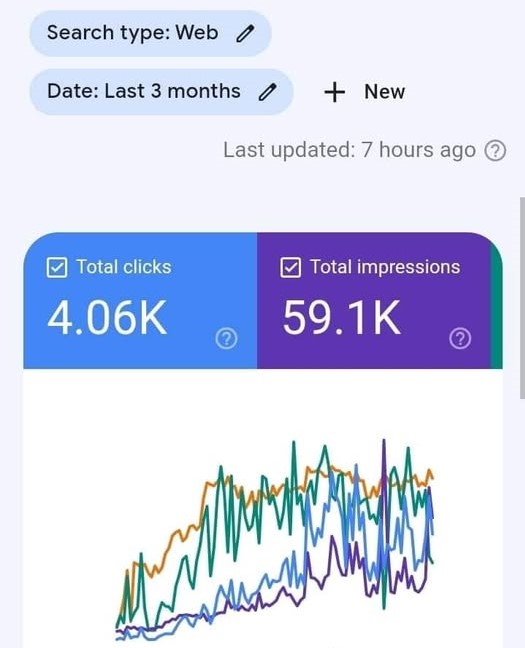
To maintain fairness and quality within our network, Fast Traffic must be run under the following conditions:
Join the Fast Traffic community today and drive high-quality, trustworthy traffic to your digital assets � the right way.